In the middle of a school year, finally in attendance, teachers and managers from the world of education are wondering what the future holds for their classes and courses.
The short answer is: more attention to education 4.0. Before the pandemic, the use of technology in education was scarce, but, during the 2020 lockdown, it began to flourish. Today, the fourth education revolution or Education 4.0 is transforming and bringing a new era of learning to Generation Z students.
3D printing in education: why?
3D printing and scanning technology has grown so rapidly that it is being talked about in all industries. Its application has become so versatile and in demand that there is a growing need for people who can understand, manage and deliver innovation through 3D printers and 3D modeling concepts. This is why education technologists and academics are working together to find better ways to engage and attract students. The adoption of different technologies in the educational sector is the way forward. So much so that the global 3D printing market is expected to grow to 15.3 million units of 3D printers shipped by 2028 *.
The growing demand is driven by applications of prototyping, functional components and production equipment in various sectors such as medical, automotive, industrial equipment, aerospace and defense, which should drive the growth of the global market. To meet these future demands, 3D printing and scanning must become a key element at all levels of academic and professional research; this will prepare students for work that requires acute critical thinking and collaborative skills.
Although 3D printing and scanning technology has not yet become a standard in higher education, its adoption by some institutes, universities and training centers is arousing much interest.
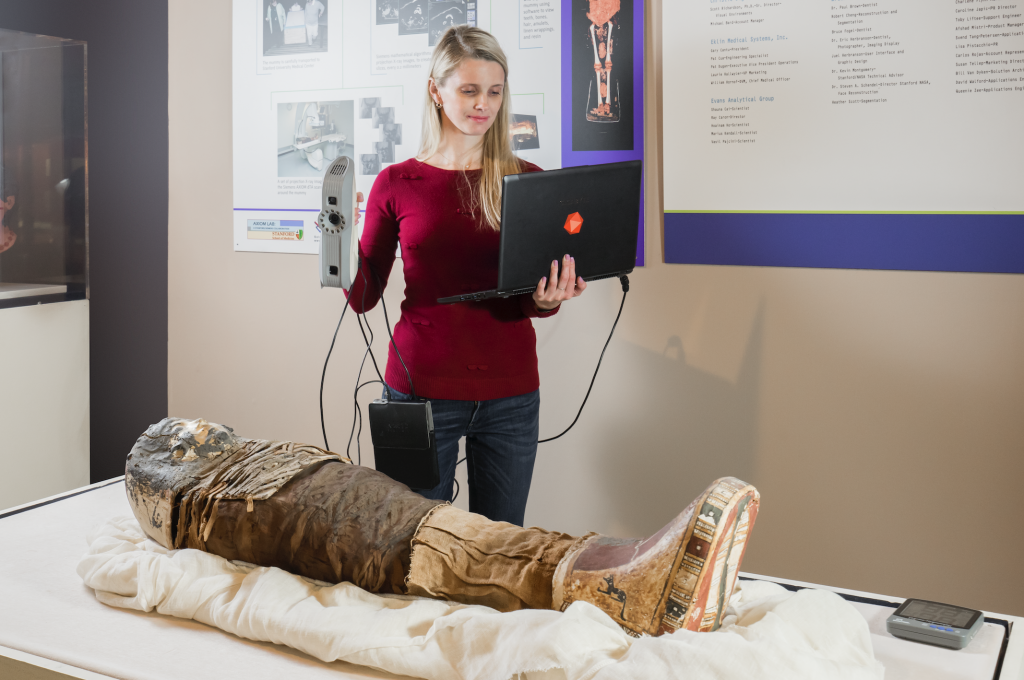
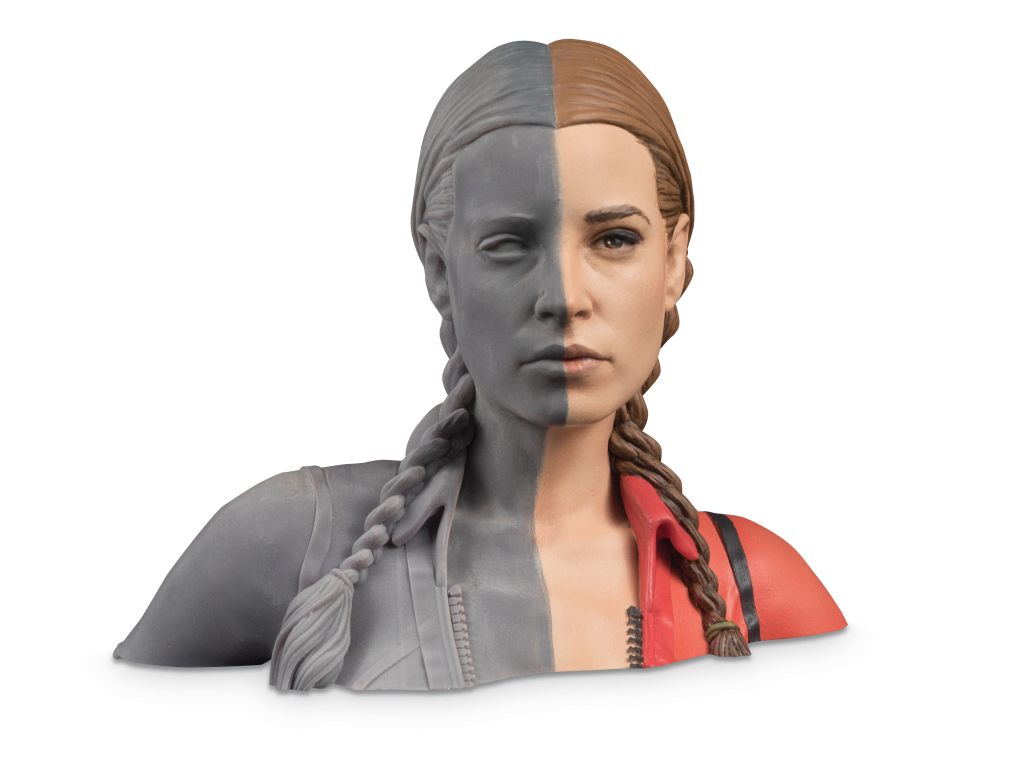
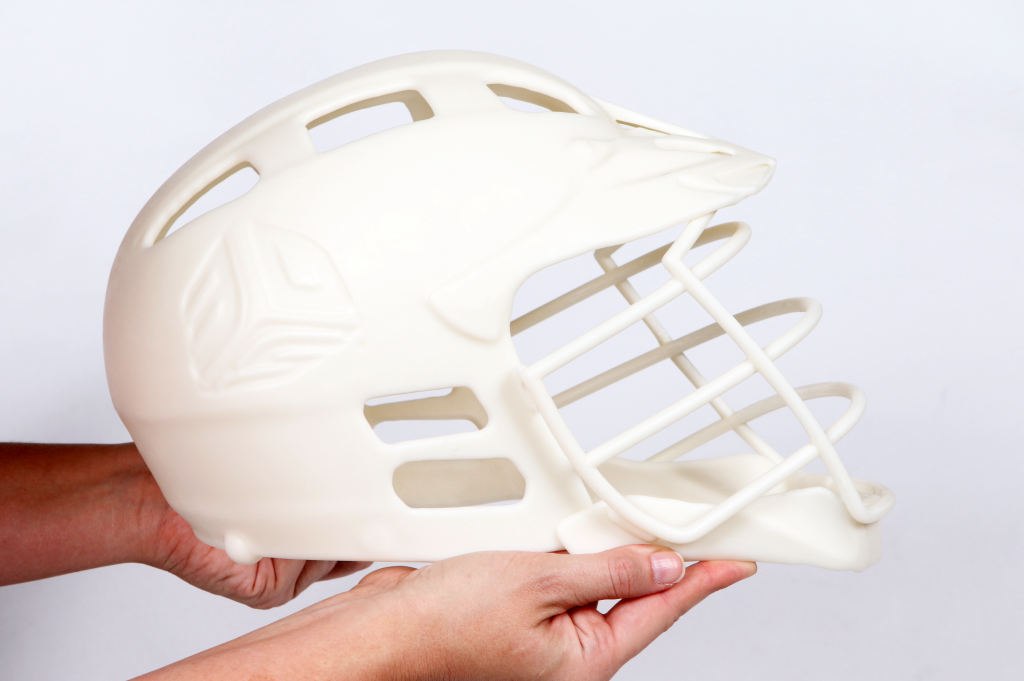
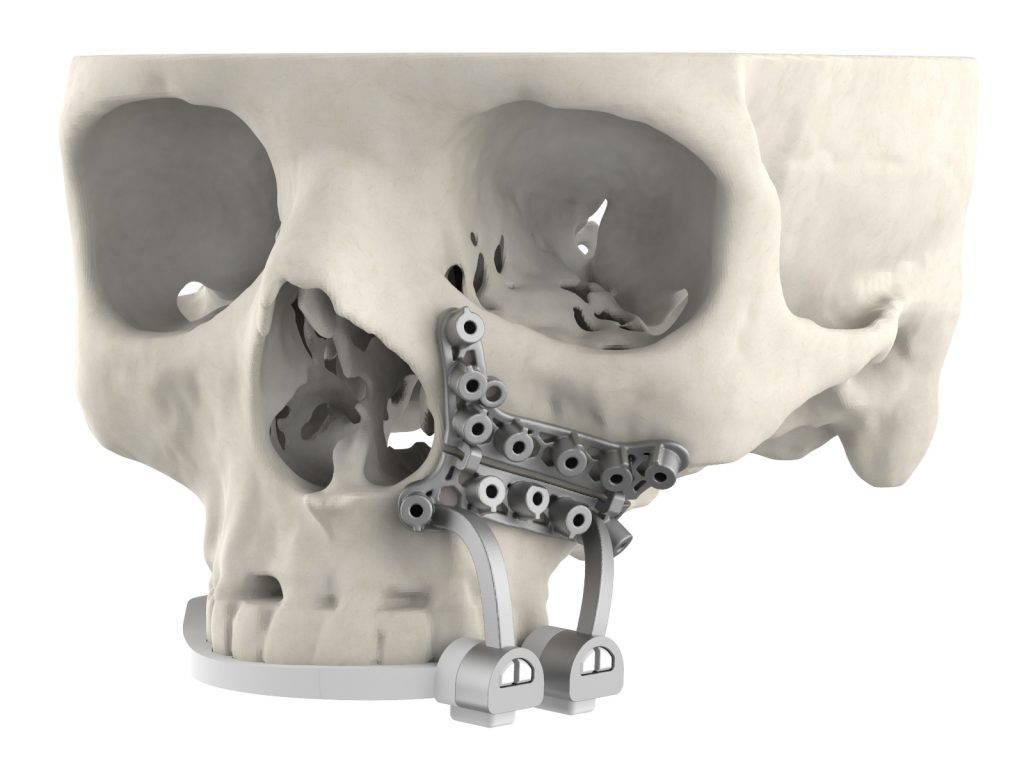
Thanks to 3D printing and scanning, teachers can design enriching learning experiences to deepen theoretical constructs, bringing learning from computer screens to the hands of students. 3D printing and design allows medical students to print organs, chemistry students to study molecules in detail, graphic design students to create 3D versions of their artwork, history students to create replicas 3D of ancient artifacts, architecture students to 3D print models of their designs, engineering students 3D prototypes, and dentistry students to have 3D printed teeth available to practice procedures such as access to the pulp chamber, root canal enlargement, irrigation and obturation of the root canal, and other procedures.
The driving force behind the exponential growth of jobs and demand in the sector is the fact that companies are also realizing the potential of 3D printers and 3D scanners, and interest is expanding enormously. Today it is already a reality that an ever-increasing number of job vacancies require professionals capable of implementing 3D printing, additive manufacturing and 3D scanning in business processes.
3D printing is making its mark in several fields, it is revolutionizing traditional learning processes and professional needs. Here are some examples:
Engineering
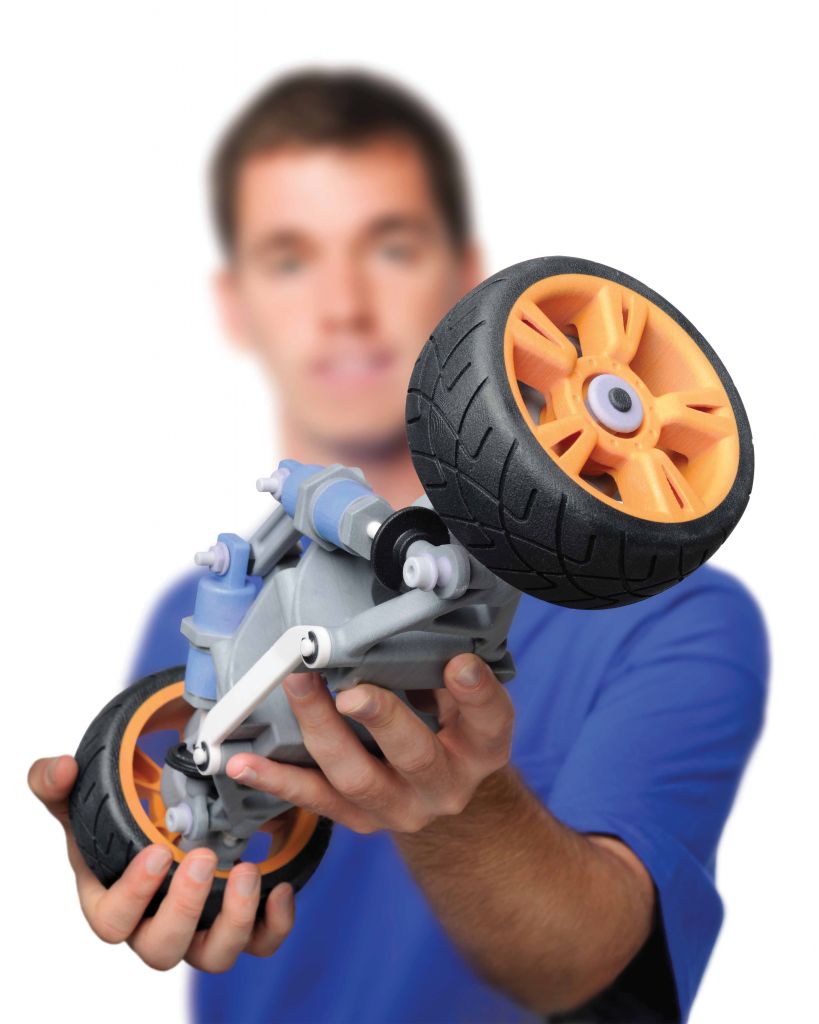
3D printers and 3D scanners are rapidly evolving technologies that require engineers who can understand, maintain and operate them. Mechanical, industrial, or computer engineers will have a better understanding of what it takes to make accurate, working models and components for prototyping, manufacturing, and design.

Biomedical technology
The constant demand for ever better treatments has become part of the growing 3D printer market. Medical researchers today are able to create functional models of organs and even functional arterial implants made from 3D materials. These new 3D technologies allow biomedical experts to lead the development of new medical solutions.
Software developers
As technology advances, the opportunities for programmers to develop cross-platform software, ever better interfaces, with ever more features, are increasing to make scanners and 3D printers easier and more efficient to use.

Animation and drawing
One sector that takes advantage of many of these tools is 3D animation, which is used in many areas, from web graphics to films. 3D design software is used to translate visual concepts into tangible objects. A training background in 3D animation allows a good understanding of the software and modeling concepts.
Seven good reasons to use 3D printing in education
What are the reasons why institutions should use 3D printing? What are the advantages of using 3D printing?
3D printing:
1. Create a hands-on learning environment
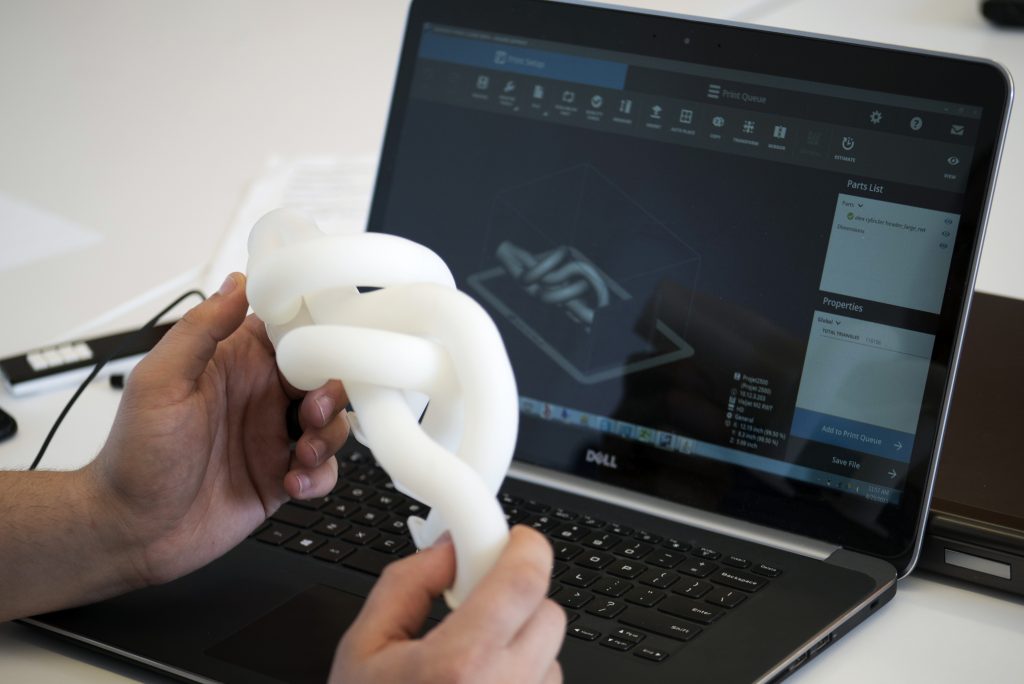
3D printing makes learning active, allowing students to use their critical thinking skills in creating their models. Engaging students in a hands-on environment supports different learning styles – both tactile and visual learners benefit greatly from 3D printing.
2. Improve creativity and innovation
Creative skills are critical to the development of a successful student. Designing models and understanding how to optimize the 3D printing process takes students’ creativity to new levels, as well as stimulating innovation.
3. Facilitates understanding of the real world. It is important that educators offer students the opportunity to better understand how to apply the acquired skills to real professional work after graduation. 3D printing is an invaluable resource for creating real-world models that can be seen and touched in all dimensions.
4. Prepare graduates for the world of work. The growth in the adoption of 3D printers will continue to drive the demand for 3D design skills. Research and development (R&D), consumer goods design and biology-related work, from organs to prosthetics, as well as architecture and construction modeling, are just some of the areas that graduates will rely heavily on. on 3D printing for prototyping. By learning to 3D print, you improve your preparation for the world of work.
5. Strengthen the digital commitment
3D printing involves learning different skills: from CAD design and post-processing. Students can learn the 3D scanning workflow, which consists of obtaining accurate measurements from a set of overlapping photos and converting them into a 3D model using a series of computer algorithms.
6. Improve problem-solving skills
Students learn how to solve problems in the real world. It was 3D printing that solved the global shortage of personal protective equipment (PPE) during the Covid-19 pandemic. Students learn how to go from an abstract idea to a 3D printed object.
7. Leverage design thinking
Collaboration is a fundamental component of design thinking. Using 3D printing, students can collaborate with their peers on assigned projects. In group projects, students learn from each other’s perspectives and different working styles. 3D printing and scanning encourage students to improve designs based on previous results and feedback.
The best 3D printing technologies for the world of education
Universities and institutes where additive manufacturing is used require fast and reliable 3D printers with particular attention to functionality.
3DZ has selected some examples of 3D technologies that may be particularly suitable for educational environments.
For metal additive manufacturing: Metal X by Markforged, a machine that allows you to easily and with maximum geometric freedom produce metal parts, either for a single part or by printing several different parts at the same time.
For SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) technology, Formlabs’ Fuse 1 printer stands out for being safe, accessible, very intuitive to use, and remarkably compact compared to other options.
With the disruptive technology of Nexa3D’s NXE400 with LSPC (Lubricant Sublayer Photo-curing), you get high resolution isotropic parts, with a large print volume, in a wide range of materials and at a print speed that makes it unique.
For 3D scanning, the leader of portable scanners is Artec 3D. Thanks to the stand-alone LEO 3D canner, easy to use, it is possible to capture large volumes, with great precision and in a short time.
For more detailed information on all the technologies available on the market and comprehensive advice on the introduction of additive manufacturing and 3D scanning in the classroom, 3DZ is one of the most experienced distributors on the market.
With the incredible boom in 3D printing in recent times, it is no wonder that educators are clamoring to include additive manufacturing in their curricula. The increase in demand for employees with additive manufacturing skills has naturally consequently led to an increase in the demand for classes with additive manufacturing skills.
Institutions are already embracing this massive educational transformation by bringing tools to the classroom that will help both students and faculty adopt the new model as quickly as possible.
3DZ, distributor and consultant in Additive Manufacturing, 3D printing and scanning with more than 10 years of experience, collaborates with more than 50 leading technical institutions and universities in Italy and abroad. Some examples are the University of Padua, the IUAV of Venice, the University of Florence, the University of Brescia, the University of Salento, the Polytechnic University of Madrid, the Polytechnic University of Catalonia, the University of Seville, the Polytechnic Institute and others.